

To add and manage applications running on the server you will also need to edit a configuration file: $ vim /usr/local/Cellar/tomcat//libexec/conf/tomcat-users.xml

Once the server is running you can navigate to the host page at: 3) – Configure Tomcat Server The version number and installation directory will have been listed by homebrew at the end of the installation output (typically the last line with a beer symbol in front). Catalina can also be set to start on system launch – although for security reasons we prefer to only run when needed (either using this command or more commonly via an IDE plugin). With replaced with your installed version. Or more generally: $ /usr/local/Cellar/tomcat//bin/catalina run $ /usr/local/Cellar/tomcat/8.5.3/bin/catalina run We are going to start the server by executing Tomcat’s Catalina command with the “run” parameter as such: $ ls /usr/local/Cellar/tomcat/
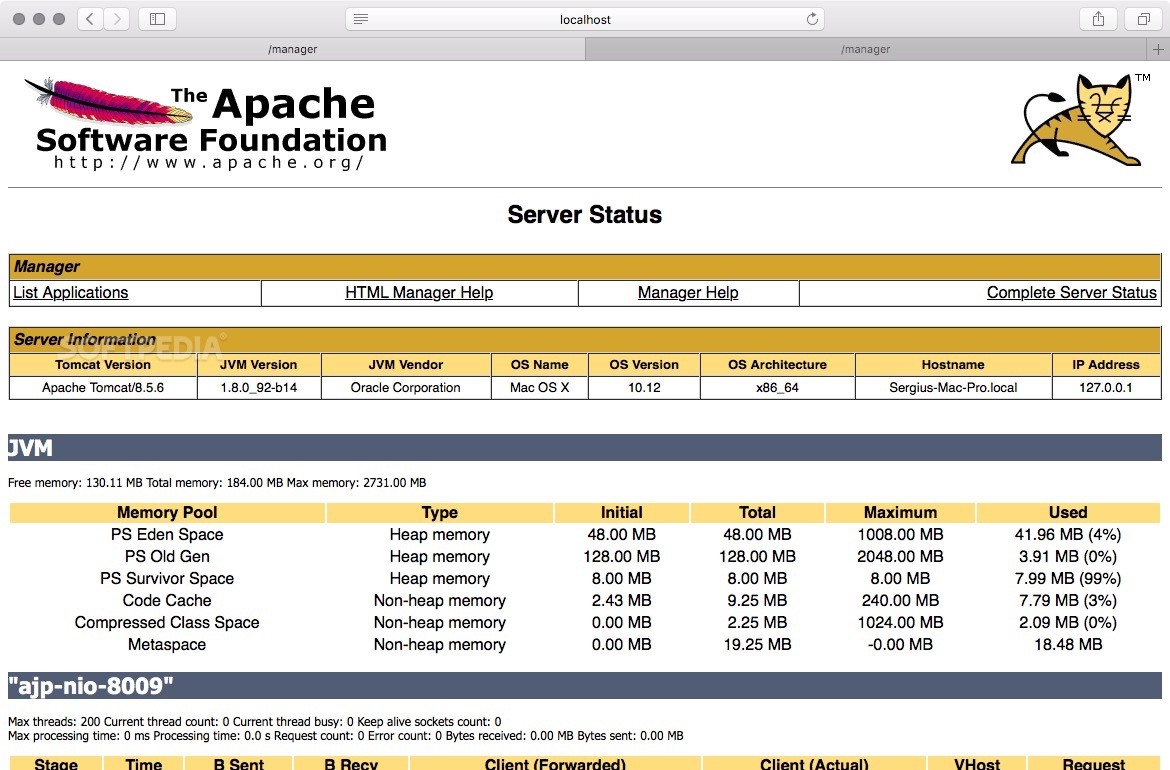
Note: to change port edit /usr/local/Cellar/tomcat/8.5.27/libexec/conf/server.xml 2) – Run Tomcat Server brew services are really useful for managing system services, type $ brew services -help for more info. Verify the Tomcat installation using homebrew’s handy “services” utility: $ brew services list It is a directory located at: $ ls /usr/local/Cellar/ Homebrew keeps packages (known as kegs) in the Cellar, where you can check config and data files. Take note of the output, brew commands are typically really good at displaying concise but useful info, error messages and help. This will take care of the downloading, installation and configuration of Tomcat and manage its dependencies as well. Install tomcat with the brew install in terminal (as a normal user, not root): $ brew install tomcat


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
